How Does Covalent Bonding Lower The Energy Of A System
How does covalent bonding lower the energy of a system. Substances with covalent bonds often form molecules with low melting and boiling points such as hydrogen and water. Formation of a bond lowers the potential energy and increase the stability of the compound. The lower energy when bonded results from the fact that atoms are more stable when their outer electron shells are full.
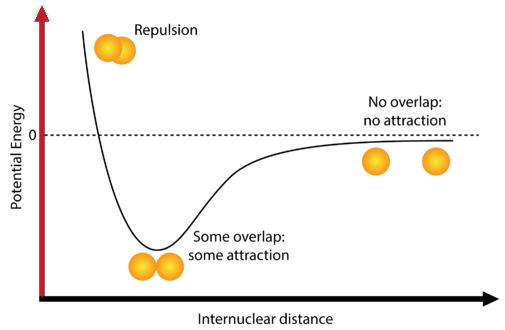
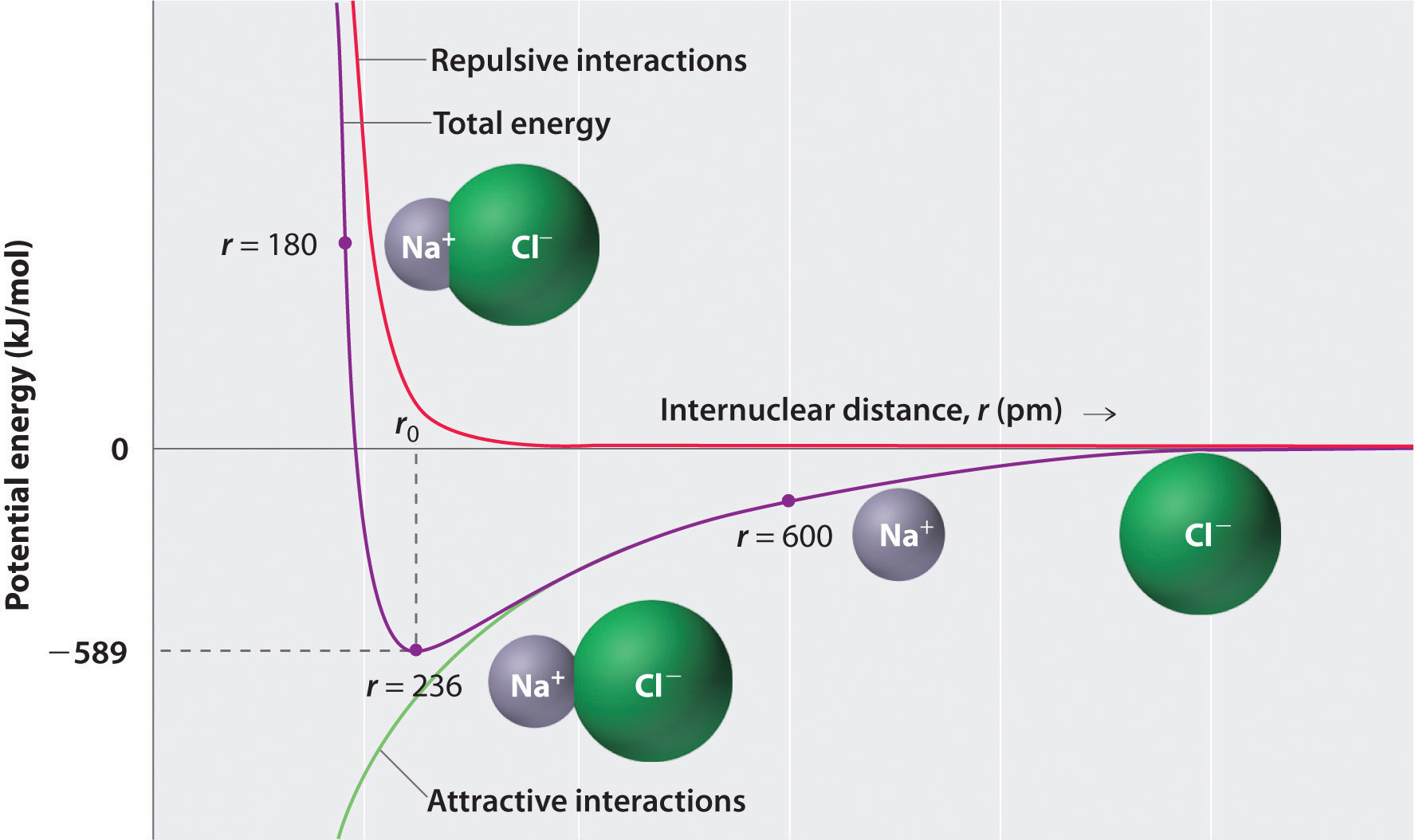
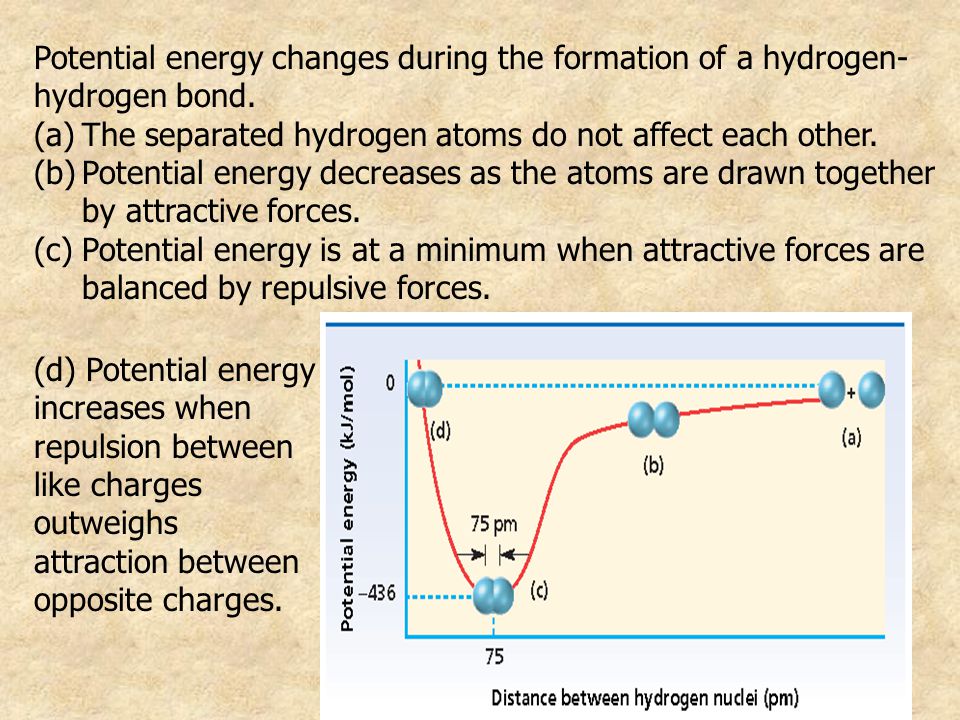
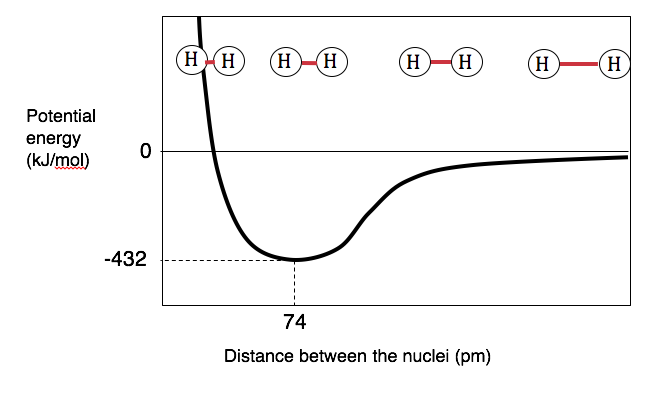
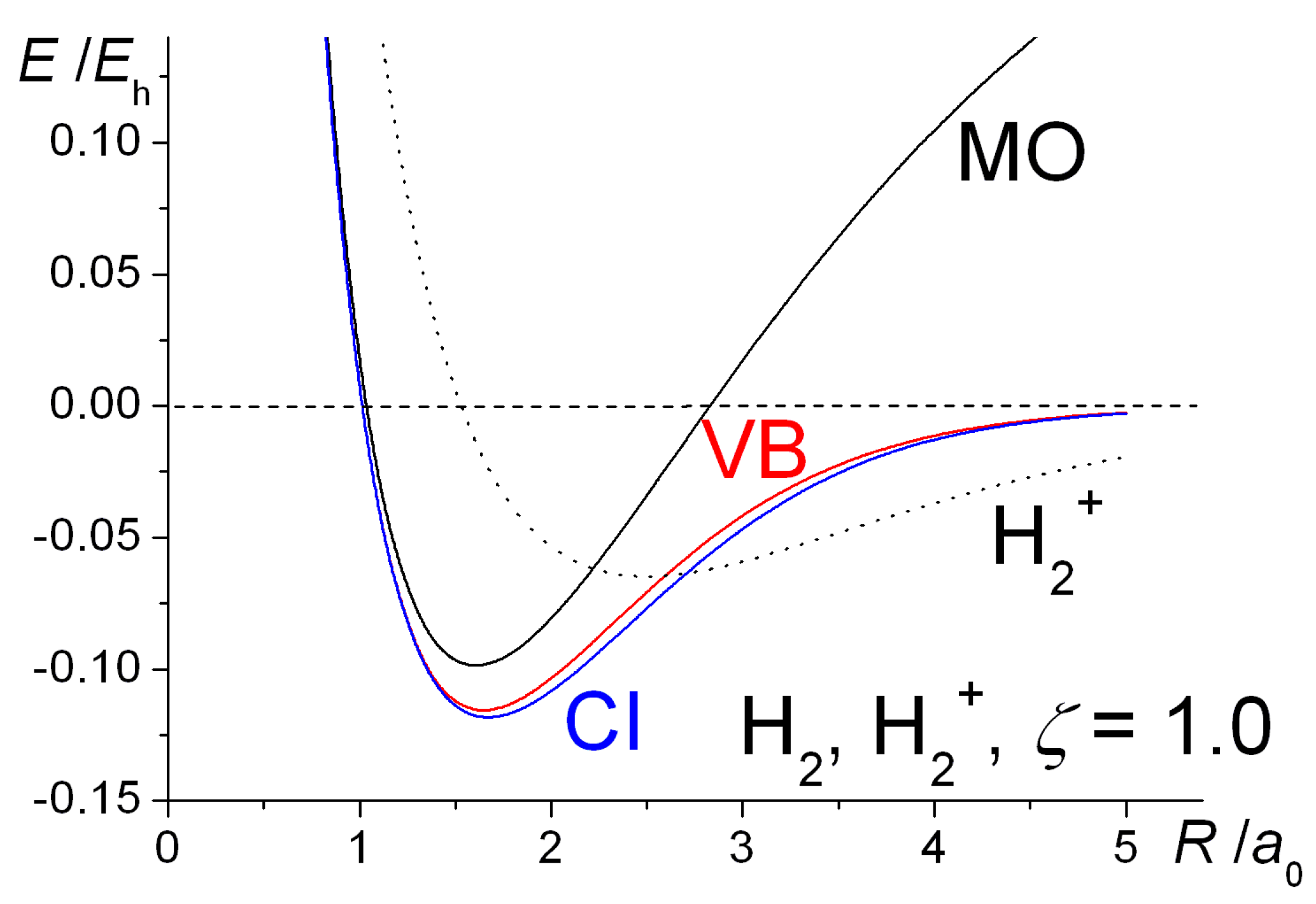
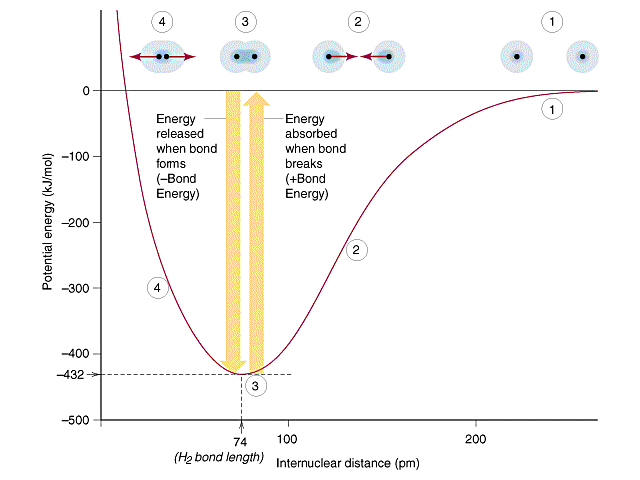
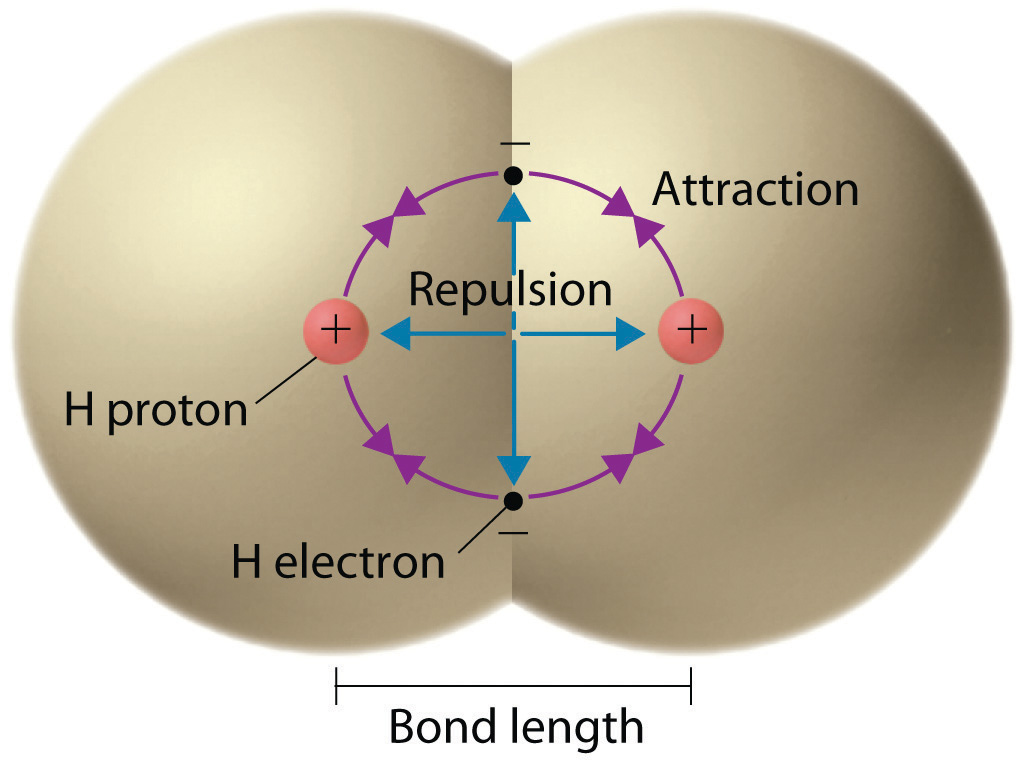
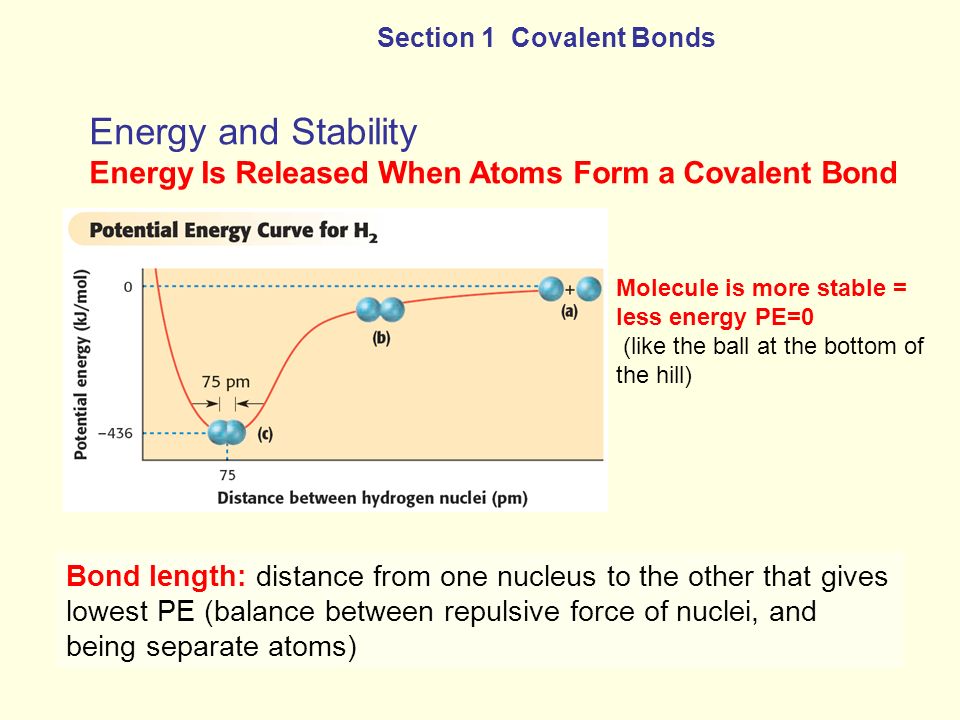
The negative charge of the electrons attracts the two nuclei closer together. When oppositely charged ions are brought together from r to r r 0 the energy of the system is lowered energy is released. According to MO theory one sigma orbital is lower in energy than either of the two isolated atomic 1s orbitals this lower sigma orbital is referred to as a bonding molecular orbital.
However the hydrogen bond strength in supercooled liquid water may be stronger than in ice 2020. This is the energy difference between the real delocalized system and the energy it would be expected to have if were not delocalized ie if it were fully localized. More stable because energy is given off when the bond is formed.
How does energy relate to bonding and chemical stability. So one atom of oxygen and two atoms of hydrogen share electrons to form a covalent molecule. In a benzene molecule the same thing happens.
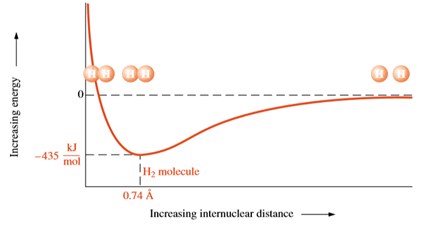
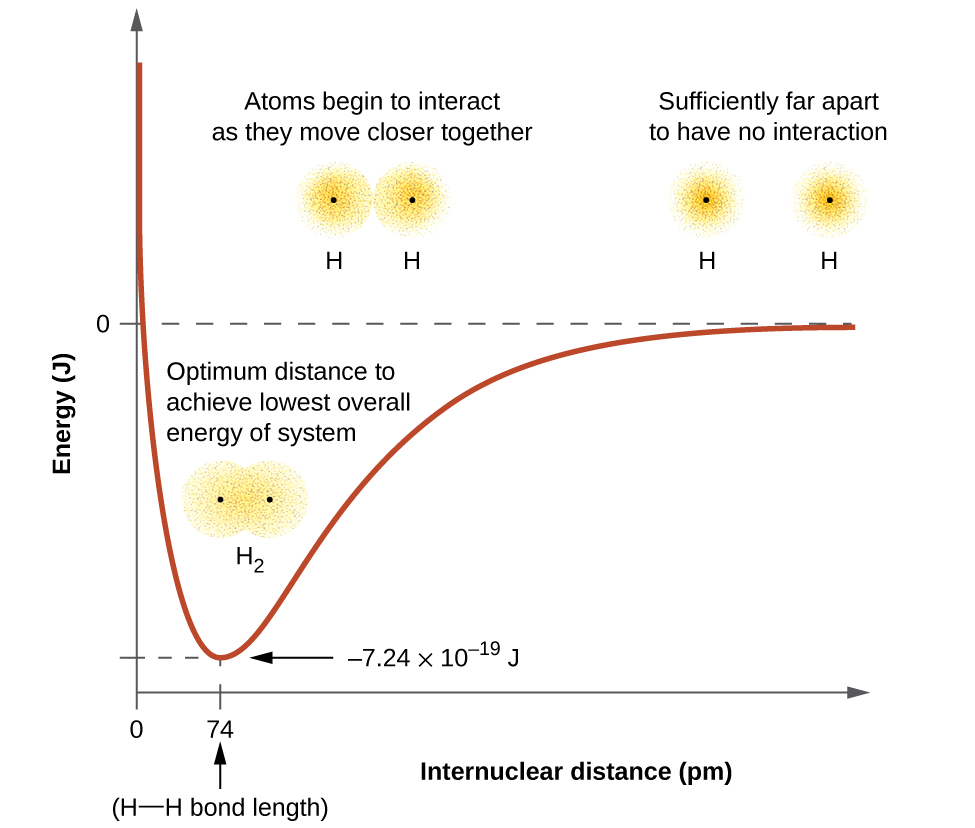
The hydrogen bonding in ice Ih is about 3 kJ mol-1 stronger than liquid water 28 kJ mol-1 at 0 K from lattice energy including non-bonded interactions and evidenced by an about 4 pm longer and hence weaker O-H covalent bond. Hence also its kinetic energy gets lower although the story doesnt end here. If the atoms continue to approach each other the positive charges in the two nuclei begin to repel each other and the potential energy increases.
The reason why a covalent bond works is because electrons are holding atoms together. The loss of energy by the electrons coincides with a simultaneous release of energy in the form of heat or light by conservation of energy. Molecular Orbital theory tells us that when you make a chemical bond between two atoms the electrons go from higher energy atomic orbitals to lower energy molecular orbitals.
Covalent bonds form between atoms when the total energy present in the newly formed molecule is lower than the energy present in each of the atoms alone. There is an excellent article by Kutzelnigg a quantum chemist on the principle behind bonding.
The negative charge of the electrons attracts the two nuclei closer together.
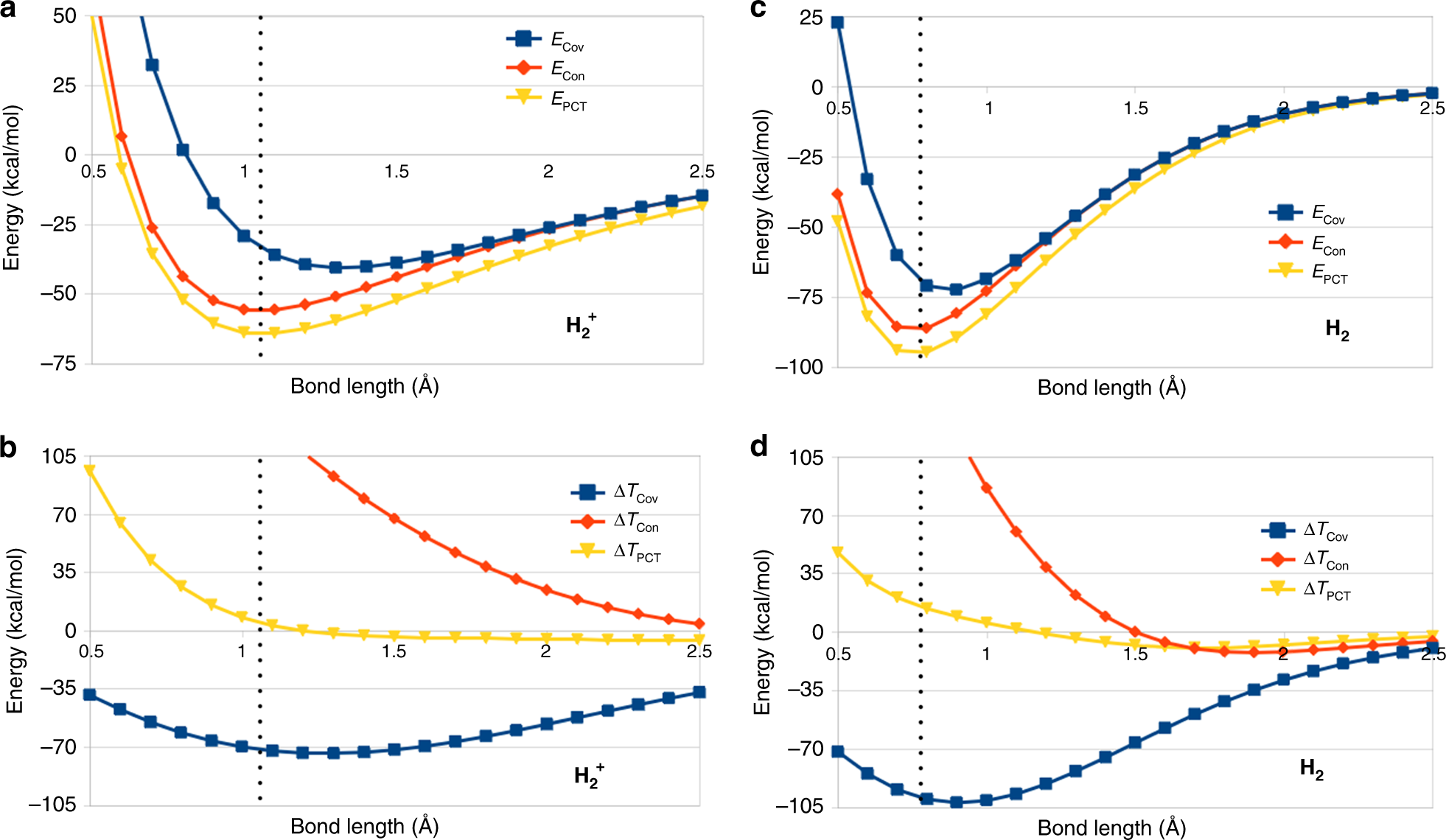
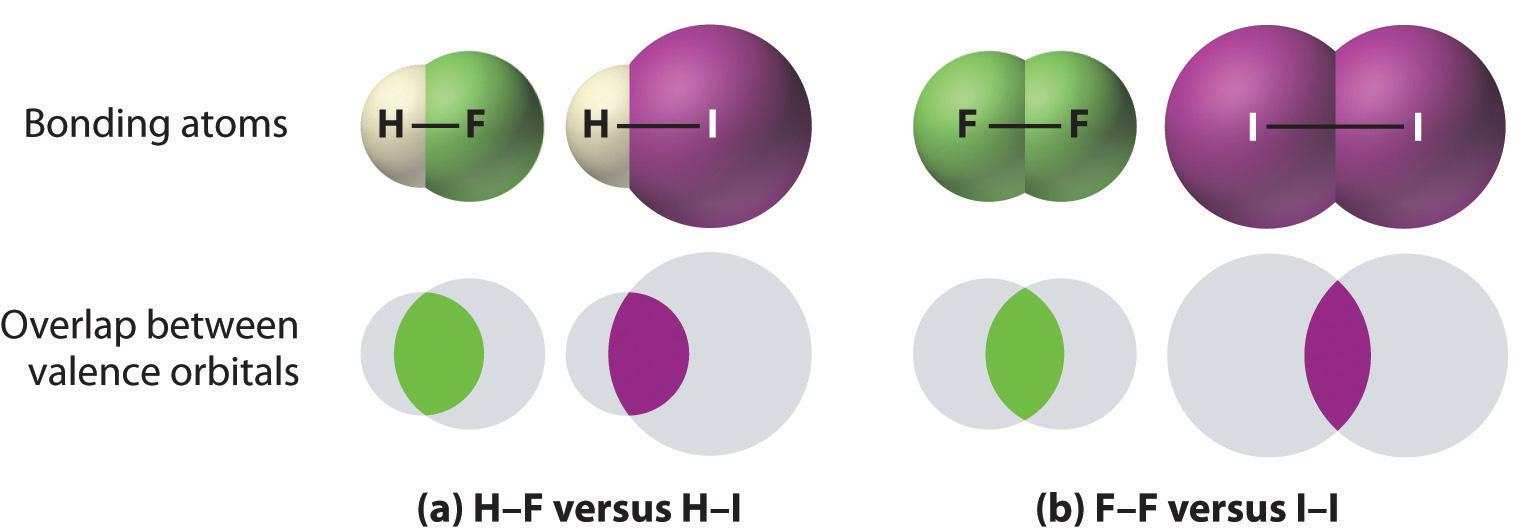
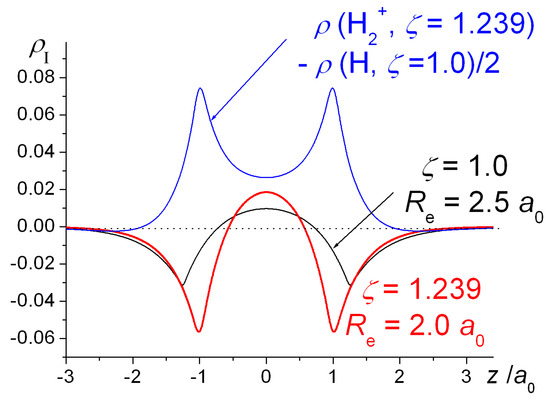
The hydrogen bonding in ice Ih is about 3 kJ mol-1 stronger than liquid water 28 kJ mol-1 at 0 K from lattice energy including non-bonded interactions and evidenced by an about 4 pm longer and hence weaker O-H covalent bond. Substances with covalent bonds often form molecules with low melting and boiling points such as hydrogen and water. A covalent bond is a bond in which two atoms share one or more pairs of electrons. Formation of a bond lowers the potential energy and increase the stability of the compound. An analysis based on the variation principle shows that in the molecules H2 H2 B2 C2 N2 O2 F2 covalent bonding is driven by the attenuation of the kinetic energy that results from the delocalization of the electronic wave function. Considering the potential energy of the interacting particles how does covalent bonding lower the energy of a system. What is the best answer below describing why covalent bonding occurs. Transferring electrons between two atoms increases attraction and causes a covalent bond. Covalent bonds form between atoms when the total energy present in the newly formed molecule is lower than the energy present in each of the atoms alone.
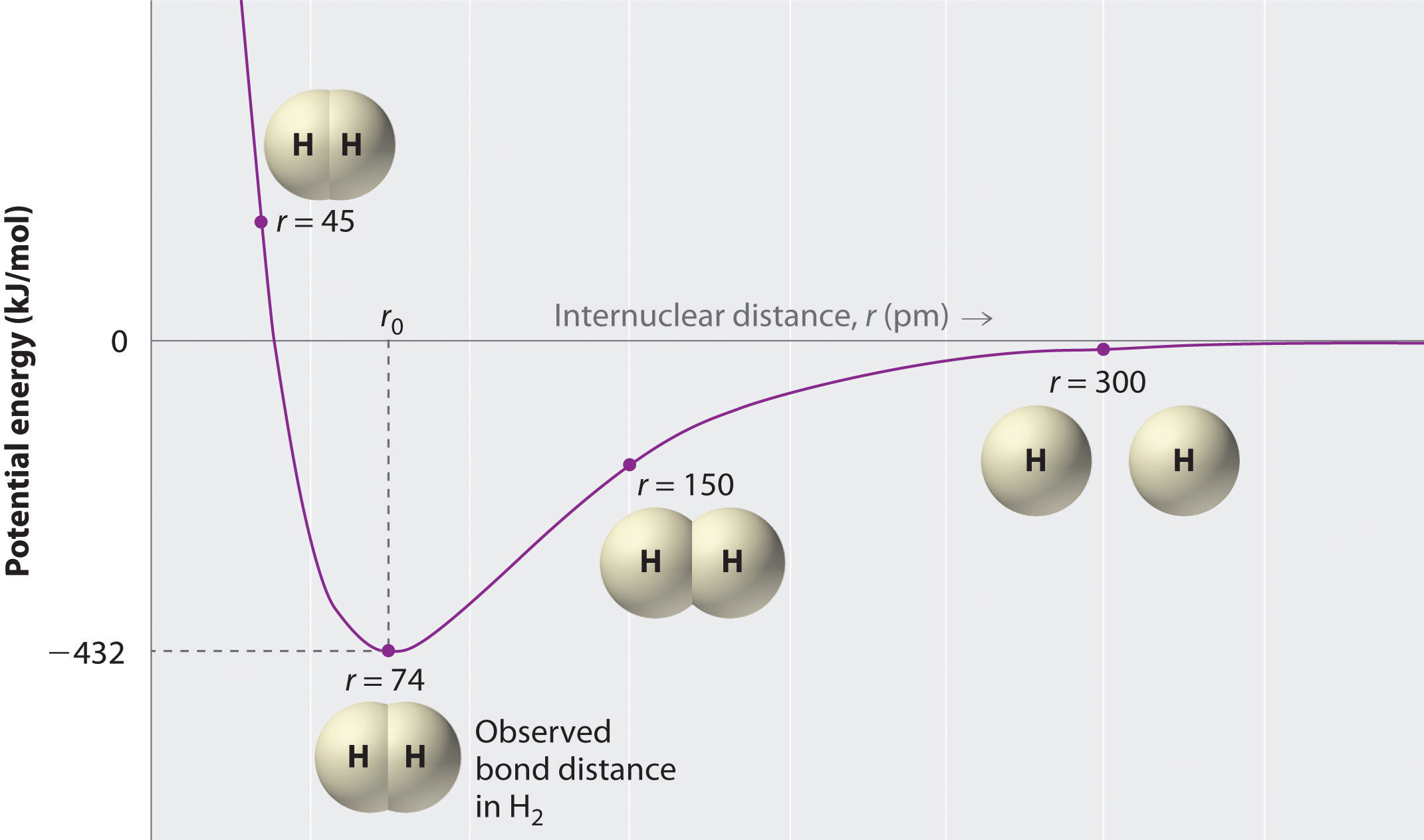
The bonding pair of electrons comes between the two atoms and screens the positive nuclei from repulsing one another. The point at which the potential energy reached its minimum represents the ideal distance between hydrogen atoms for a stable chemical bond to occur. What is a diatomic molecule. Molecular Orbital theory tells us that when you make a chemical bond between two atoms the electrons go from higher energy atomic orbitals to lower energy molecular orbitals. Transferring electrons between two atoms increases attraction and causes a covalent bond. So one atom of oxygen and two atoms of hydrogen share electrons to form a covalent molecule. How does energy relate to bonding and chemical stability.
























Post a Comment for "How Does Covalent Bonding Lower The Energy Of A System"